July 23rd news: The Quark Health Large Model has successfully passed the written examination of 12 core medical disciplines by chief physicians in China, becoming the first large model in the country to complete this challenge. Currently, the "Chief-level AI Doctor" capability has been fully integrated into Quark's AI search, and users can call it by selecting deep search when querying health-related questions.
This is another leap in the capabilities of the Quark Health Large Model, following its success in passing the associate chief physician qualification exam in May. In comparison with vertical and general models, the Quark Health Large Model shows a performance curve where the higher the difficulty, the more significant the advantage, demonstrating breakthroughs in complex medical reasoning tasks.
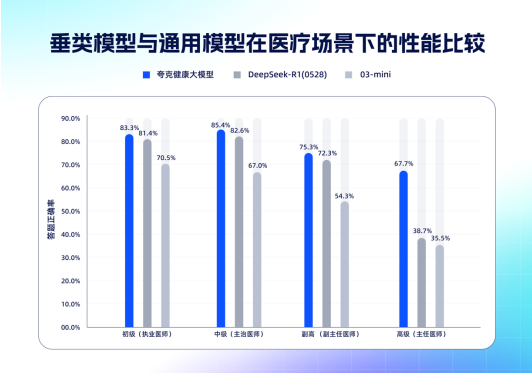
This reveals the great potential of developing vertical models in the medical field. Based on Qwen, the Quark Health Large Model has taken a deep engineering approach tailored for specific scenarios. "We are not training AI to answer medical questions, but to learn medical thinking," said Xu Jian, head of Quark's health algorithm team.
One of the core breakthroughs of the Quark Health Large Model is the development of a "slow thinking ability." This ability integrates chain reasoning and multi-stage clinical deductive path modeling, enabling the model to analyze complex medical problems in stages and gradually arrive at the final answer.
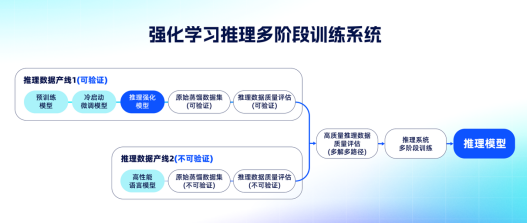
The foundation for building the slow thinking ability is having high-quality reasoning training data. To this end, Quark has established an engineering system called "dual data production lines + dual reward mechanisms." On one hand, medical data is divided into "verifiable" and "non-verifiable" categories, corresponding to diagnostic tasks and health advice tasks respectively; on the other hand, the training methods introduce "process reward models" and "result reward models," which evaluate the rationality of the model's reasoning chain and the accuracy of the final conclusion, significantly improving the model's clinical explainability and reasoning consistency.
This system also includes a multi-stage reinforcement learning process, including strict manual verification of cold-start data, multi-round sample screening and difficulty-increasing training strategies, as well as a cheating detection mechanism to prevent "high-score speculation." Through real doctor annotations and "question-think-answer" group data-driven reinforcement learning, the Quark Health Large Model not only learned medical knowledge, but also mastered the path selection, evidence integration, and balance of multiple solutions in medical thinking. The underlying authoritative medical knowledge base ensures that the model's output is professional and up-to-date.
Professor Xie Jinsheng, chief physician of the Department of Cardiac Surgery at Anzhen Hospital, believes that Quark's answers are more professional than those of some specialist doctors. This achievement is backed by the deep involvement of professional physician teams. Currently, the Quark Health Large Model has a professional physician annotation team of thousands, with over 400 being senior medical experts with titles of associate chief physician or above.
Thanks to its professionalism in the medical field, Quark AI Search has attracted a large number of medical students and doctors. Zhao Cunzhong, head of Quark Health operations, introduced that the platform's monthly active users among medical students across the country have exceeded 2 million, with coverage over half, and they widely use Quark for basic knowledge searches, exam preparation, and clinical assistance in diagnosis.
