Recently, the LongCat team of Meituan officially launched a smart agent evaluation benchmark called VitaBench, aimed at multi-interaction tasks, especially applications in complex life scenarios. The launch of VitaBench provides an important infrastructure for the development of smart agents in real-life scenarios.
VitaBench focuses on high-frequency real scenarios such as food delivery, dining in restaurants, and travel. It has built an interactive evaluation environment with 66 tools. The design of evaluation tasks covers complex operations such as ticket purchasing and restaurant reservations, requiring smart agents to demonstrate comprehensive performance in deep reasoning, tool calls, and user interaction during task execution.
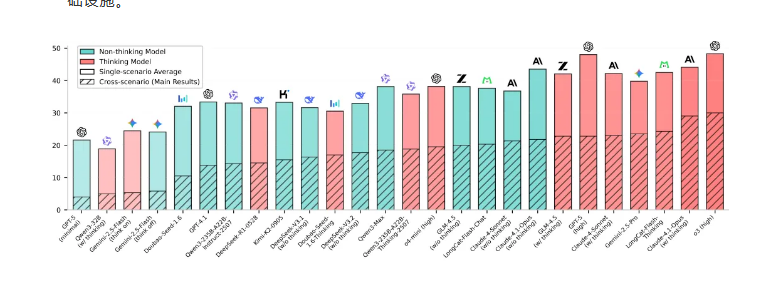
Although leading reasoning models have made some progress, research by the LongCat team shows that the success rate of smart agents in complex cross-scenario tasks is still below 30%, indicating a significant gap between current technology and practical application needs. The development of VitaBench aims to address this issue and fill the gap between existing smart agent evaluation benchmarks and real-life application scenarios.

The design of this benchmark is based on an in-depth analysis of three dimensions: reasoning complexity, tool complexity, and interaction complexity. By quantifying these dimensions, the team systematically measures the performance of smart agents in real scenarios. For example, reasoning complexity is mainly evaluated by the need for information integration, the size of the observation space, and the number of reasoning points required; tool complexity considers the dependency relationships and the length of the call chain of tools; and interaction complexity focuses on the ability of the smart agent to respond in multi-turn dialogues.
The construction of VitaBench involves two stages: first, the design of the tool definition, followed by the creation of tasks and the establishment of evaluation criteria. This process ensures the diversity and complexity of tasks while avoiding the limitations of traditional document modes, allowing smart agents to independently reason and make decisions without redundant rules.
Currently, VitaBench is fully open source, and researchers and developers can access related resources through its official website and GitHub. The release of VitaBench marks an important milestone in the field of smart agent evaluation and is expected to promote further application and development of smart agent technology in real-life scenarios.
Project homepage: https://vitabench.github.io
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.26490
Code repository: https://github.com/meituan-longcat/vitabench
Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/meituan- longcat/VitaBench
Leaderboard: https://vitabench.github.io/#Leaderboard









