Recently, Moonshot AI released a new hybrid linear attention architecture called "Kimi Linear." This architecture is claimed to outperform traditional full-attention methods in handling short-range, long-range information, and various scenarios such as reinforcement learning (RL). Its core technology, Kimi Delta Attention (KDA), is an optimization of Gated DeltaNet, introducing a more efficient gating mechanism to better manage the memory usage of limited-state RNNs.
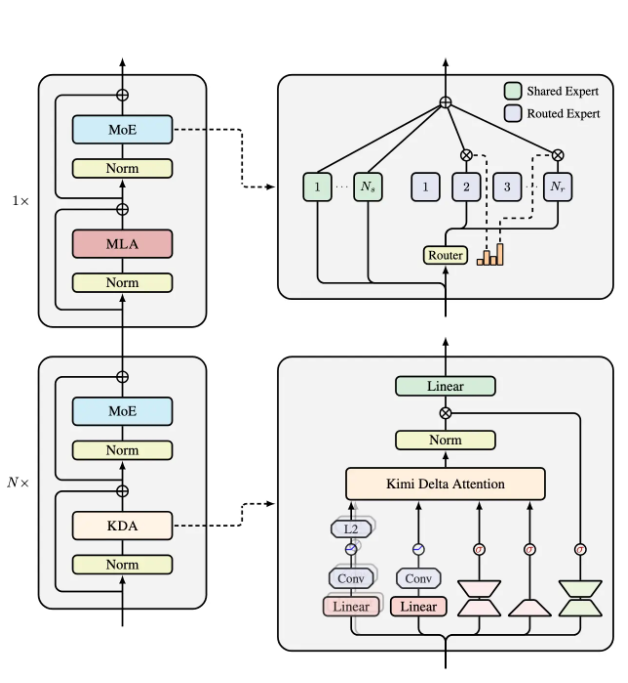
Kimi Linear is composed of three Kimi Delta Attention units and one global MLA. This structure compresses the memory of limited-state RNNs through fine-grained gating, making the model more efficient when processing information. According to official statements, in a 1M token data scenario, the KV cache usage of Kimi Linear is reduced by 75%, and the decoding throughput can be increased up to six times. TPOT is accelerated by 6.3 times compared to traditional MLA.
This new architecture provides stronger support for various AI application scenarios. Whether in information-intensive natural language processing tasks or reinforcement learning in dynamic environments, Kimi Linear shows significant advantages. As AI technology continues to develop, this efficient attention mechanism may bring new breakthroughs for future intelligent applications.
More technical details can be found in the technical report of Kimi Linear at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-Linear/blob/master/tech_report.pdf.
Key Points:
🌟 Kimi Linear is a new hybrid linear attention architecture that optimizes information processing performance.
🚀 In a 1M token scenario, the KV cache usage is reduced by 75%, and the decoding throughput is increased by six times.
🔍 Kimi Delta Attention is its core technology, which optimizes RNN memory management through fine-grained gating.


