The Google Research team, in collaboration with researchers from the University of California, Santa Cruz, has launched DeepSomatic, an innovative artificial intelligence model designed to identify genetic variations in cancer cells. In a collaborative study with Children's Hospital, DeepSomatic successfully identified 10 pediatric leukemia cell mutations that other tools failed to detect.
DeepSomatic uses a small variant caller tailored for cancer genomes, compatible with Illumina short reads, PacBio HiFi long reads, and Oxford Nanopore long reads. This approach extends DeepVariant, enabling the detection of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (indels), supporting tumor-normal and tumor-only workflows, including formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) models.
DeepSomatic works by converting aligned reads into image-like tensors, which encode stacking, base quality, and alignment context. Through a convolutional neural network, the model classifies candidate sites as somatic variants or non-variants, ultimately generating VCF or gVCF files. This design makes DeepSomatic highly adaptable across technical platforms, as the tensor can summarize local haplotype and error patterns across different technologies.
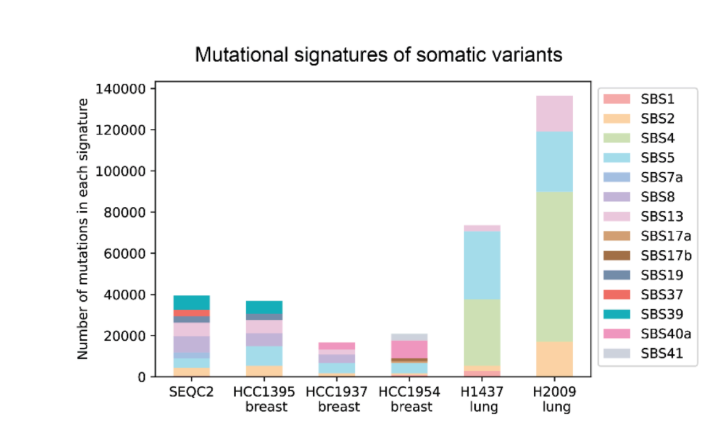
In terms of datasets and benchmarking, DeepSomatic is trained and evaluated using the CASTLE (Cancer Standard Long Read Evaluation) dataset. This dataset includes six pairs of matched tumor and normal cell lines, with whole-genome sequencing performed on Illumina, PacBio HiFi, and Oxford Nanopore. The research team has released benchmark sets and access for other researchers to reuse, filling a gap in multi-technology somatic training and testing resources.
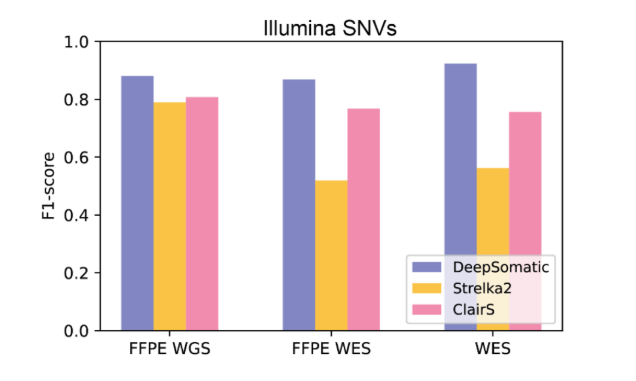
The results show that DeepSomatic outperforms currently widely used methods in detecting single nucleotide variants and small insertions and deletions. For example, in insertion-deletion detection on Illumina sequencing, DeepSomatic achieved an F1 score of about 90%, while other methods reached only 80%; on PacBio sequencing, DeepSomatic's F1 score exceeded 80%. The research team also reported the discovery of 329,011 somatic variants, further validating DeepSomatic's strong capability in insertion-deletion detection.
Research: https://research.google/blog/using-ai-to-identify-genetic-variants-in-tumors-with-deepsomatic/
Key Points:
🌟 DeepSomatic can identify various genetic variations in cancer cells, covering multiple sequencing platforms.
🔍 The model uses a convolutional neural network to convert read information into image-like tensors, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
📊 In benchmark tests, DeepSomatic's detection accuracy significantly exceeds existing mainstream methods, especially in insertion-deletion detection.









