Recently, DeepSeek released a new OCR document understanding model - DeepSeek-OCR. The model not only achieves top performance in image document parsing, but also introduces a bold and highly innovative concept: "Visual Memory Compression" mechanism, aiming to revolutionarily solve the problem of explosive growth of computational resources when large language models (LLM) process ultra-long contexts.

Core Breakthrough: Enabling AI to "Read by Looking at Images" with Efficient Compression
The core innovation of DeepSeek-OCR lies in mimicking the human visual memory mechanism, compressing long text information into an image space, thereby significantly reducing the consumption of "Token" for language models.
Summary of Working Principle:
This mechanism works by "drawing text as images": first, the long text is compressed into a single image; then, a visual model compresses this image into the minimum number of "visual tokens" (Visual Tokens); finally, the language model decodes and restores the text from these visual tokens.
In other words, this technology enables the model to **"read by looking at pictures"**, rather than the traditional "word-by-word reading", greatly improving the efficiency of information processing.
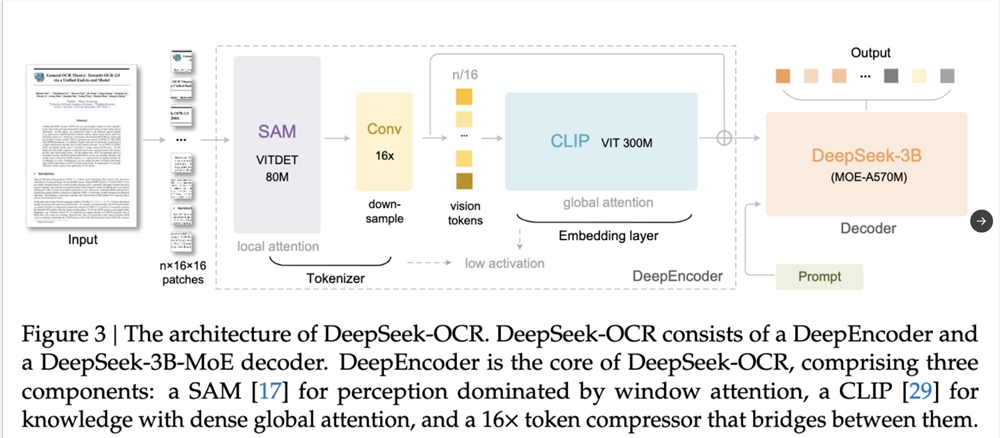
Remarkable Performance: 10x Compression and Future Potential
DeepSeek demonstrated remarkable compression results: an article of 1000 words was compressed into a single image, requiring only 100 visual tokens (achieving 10x compression) to represent it, and the model could still recover 97% of the original text during decompression.
This breakthrough not only demonstrates the effectiveness of the "visual memory compression," but also reveals its huge potential for the future development of AI:
Resolving LLM Memory Limitations: It has the potential to become a key technology to break through the "memory limitations" of large models, enabling AI to process ultra-long contexts of hundreds of pages with less computational power.
Future AI Memory Storage: In the future, AI could store old memories as images, achieving efficient information archiving.
Analogy to Human "Forgetting Curve": High-Fidelity and Low-Density Memory
DeepSeek compares this visual compression mechanism to the human "forgetting curve", cleverly simulating the natural memory and forgetting processes of humans:
High-Fidelity Memory: Recent context is preserved as high-resolution images, i.e., high-fidelity information.
Low-Density Memory: Older context is compressed into blurry images, i.e., low information density.









